Understanding Rabies Virus
Rabies is a highly lethal viral disease affecting the central nervous system. The virus primarily targets neurons, causing severe inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). Initial symptoms manifest as fever and localized tingling, progressing to severe neurological symptoms including aggressive behavior, hydrophobia, paralysis, and ultimately, death if left untreated.
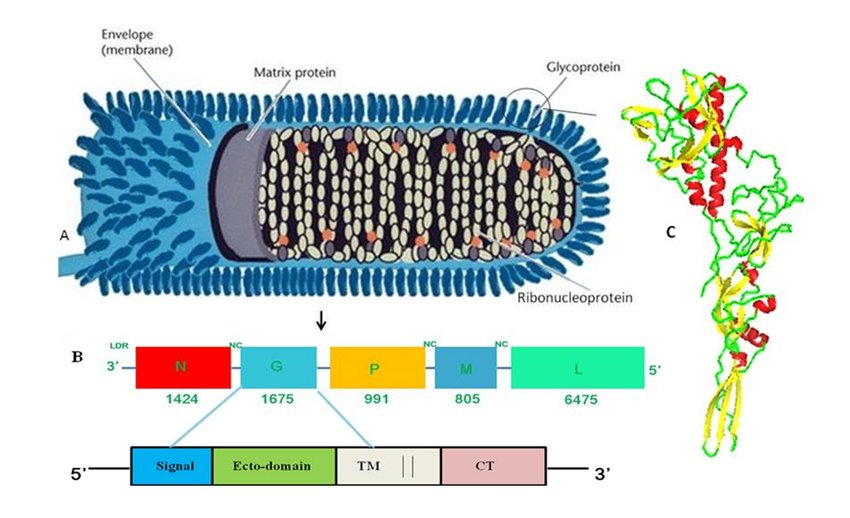
Transmission occurs through direct contact with infected saliva, typically via bites or scratches from rabid animals. The virus can also enter through mucous membranes or open wounds. Once symptoms appear, the disease is almost invariably fatal, making early detection and prevention crucial for survival.